Knee joint arthroscopy
Every year people‘s life is getting more active. There is getting more people involved in various technical and extreme sports and looking for forms of active leisure time. Therefore, it is obvious that a number of various traumas is getting increased as well. Regardless circumstances where traumas are incurred (during the sports competitions or leisure time), they have to be treated in the same methods.
Traumas of joints of the knee, shoulder and ankle happen most commonly. Our goal is to return a patient into the normal active life as soon as possible. In order to do it, a diagnosis has to be determined very precisely and the most optimal treatment way (conservative or surgical) has to be chosen.
Arthroscopy, the minimally traumatizing surgical technique, is used for surgery operations of joints.
What is arthroscopy?
Arthroscopy is a surgical intervention, which is performed by the surgeon, inside the joint through incisions in size of 0,5-1cm. It is a method of minimal invasion, being performed with arthroscope and other arthroscopic equipment. Arhroscope is a small instrument in the size of a pencil with included video camera. Arthroscopies of joints of the knee, shoulder, ankle and elbow are most common (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Two incisions of 0,5-1 cm each are used for performance of arthroscopy of the knee joint.
The reasons for performance of arthroscopies of the knee joint
Torn menisci
The most common reason for performance of arthroscopy is torn menisci. Menisci consist of two semilunar-shaped, similar to cartilage, sections (Figure 2).
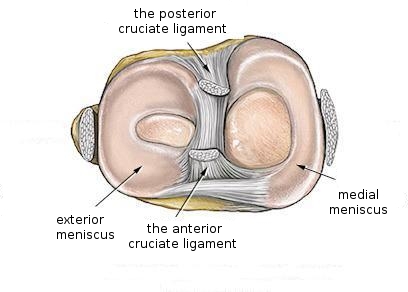
Figure 2. Anatomy of the knee joint
Torn menisci can cause pain n the knee joint, swelling, seizing and discomfort during walking. In case of torn menisci, if the medicine was used, the pain can decrease; however, the symptoms intensify if the knee joint is turned improperly. Torn menisci do not recover themselves. Depending on the type of tearing (A, B, C and D in the Figure 3, Figure 4, Video l), menisci may be sewn or the torn part of them may be removed (Figures 5 and 6). After surgery operation the patient can fully flex the operated knee joint and step the leg. The next day after operation the patient is allowed to go home for ambulant treatment.
Figure 3. The types of meniscus tears
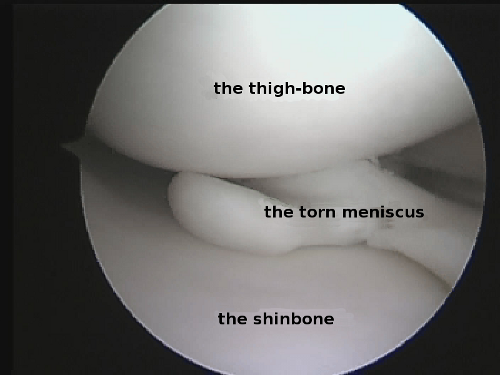
Figure 4. “Tongue”-type tear of the medial meniscus
Video 1. Tear of medial meniscus of the knee joint

Figure 5. The view after resection of a torn part of the medial meniscus

Figure 6. The view after fixation of external meniscus
Torn ligaments
Ligaments provide stability to the knee joint (Video 2).
Video 2. Anatomy of the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments of the knee joint
The anterior cruciate ligament and medial collateral ligament are damaged more frequently and the posterior cruciate ligament and lateral collateral ligament are damaged less. In most cases the trauma happens during sports activity. Damages of the anterior cruciate ligament cause instability, pain and swelling of the knee joint, due to which physical activity of the patient is decreased, unreliability in the limb appears, there is a fear to step the leg improperly causing instability episode. After decrease of the load, thigh muscles languish, and it impacts showing up the symptoms. In long delay, the pain of nagging and sharp character may appear, as every episode of instability may mechanically damage cartilages and menisci. Resorptive implants, which “melt” in 1,5 years, or Endobutton system are used for operation (Video 3, Video 4, Figure 7).
Video 3. Tear of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee joint
Video 4. The view after plastic surgery of the anterior cruciate ligament

Figure 7. 3 incisions including 2 incisions of 0,5 cm each and one incision of 2-3 cm that are used for anterior cruciate ligament .
Plastics of anterior cruciate ligament may be performed in two ways: using one or two bundles, in consideration of the patient’s physical activity (Figures 11 and 12).
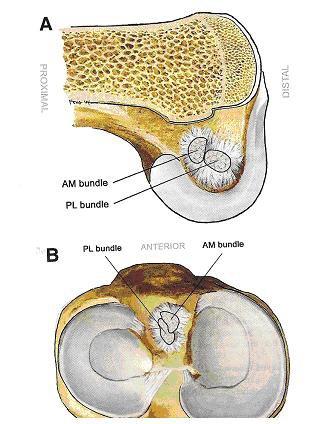
Figure 11. Anatomy of the anterior cruciate ligament

Figure 12. Double-bundle reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament
Damages to the patella
Given damage to the patellar cartilage, squaring of knees leads to pain. During arthroscopy, the patellar cartilage is dubbed as well as the patella’s position at movement is estimated. Pathological position of the patella may be corrected (Figure 8, Figure 9).
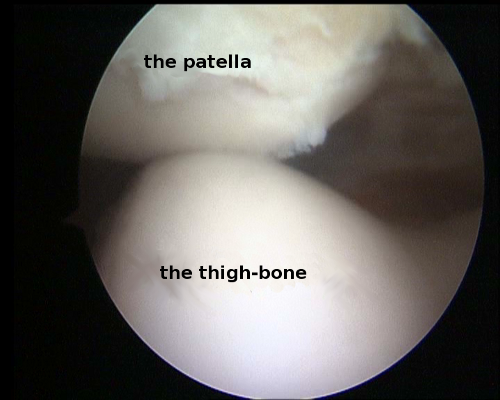
Figure 9. Faulty position of the patella
Defects of the surface of the articulate cartilage
Defects of the surface of the articulate cartilage are most often symptoms of osteoarthritis. In the course of time, the cartilage wears down; pain of sharp and nagging character appears. The pain gets more intensive after longer walk or standing. During arthroscopy, an extent and a degree of damage of the articulate cartilage is estimated. During surgery operation, the cartilage may be dubbed or other procedure, chosen by the surgeon during the operation, may be performed (Figure 10).

Figure 10. The view of arthrosis in the knee joint
There are also many other reasons that cause to suffer from troubles of the knee joint, which may be diagnosed only by specialists.
|